sketch-lib
Author: Alex Dumitrache, alex@cimr.pub.ro
License: GPL
Download
You may download the library in zip format.
You may also clone the project with Git by running:
$ git clone git://github.com/alexdu/sketch-lib
Usage
First, you have to copy lib/ into your working folder.
Then, include lib/defaults.sk and lib/objects.sk in your file, and use language tikz in global options section. See the examples below.
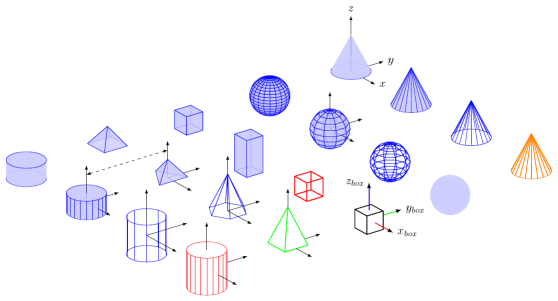
First program
def blue<>
input{lib/defaults.sk}
input{lib/objects.sk}
{pyramid}
global {
language tikz
camera view((3,-2,1), (o), [Z])
}
Compiling the program
Save the program as pyramid.sk and compile it using -T option:
$ sketch -T pyramid.sk -o pyramid.tex
Now you are ready process pyramid.tex with pdflatex.
For advanced options, see the sketch manual.
You may also use sk2pdf or sk2png to obtain the PDF or PNG directly from .sk source:
$ sk2pdf pyramid.sk
Constants
The library defines the following constants:
(o) (x) (y) (z)- (0,0,0), (1,0,0), (0,1,0) and (0,0,1) as points[O] [X] [Y] [Z]- the same values, as vectors
The unit vectors are useful for transformations:
rotate(30, [X])Styles and options
Before including the library, you will define a tag for selecting the style. Available styles:
blue<>red<>gray<>
Caveat: you may only select the style by name at before including lib/defaults.sk.
However, you may redefine style for each object.
Another option is to show the objects in wireframe (without hidden line removal):
wireframe<>
You may use this option:
-
Before including
lib/objects.skor at the beginning on the file. In this case, the entire scene will be drawn in wireframe. -
For each object individually (more on this later).
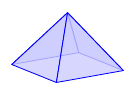
Source: styles.sk
In the figure:
- top row: default style (when you don’t define any),
blue<>,red<>,gray<> - bottom row: the same styles, with
wireframe<>tag defined
Objects
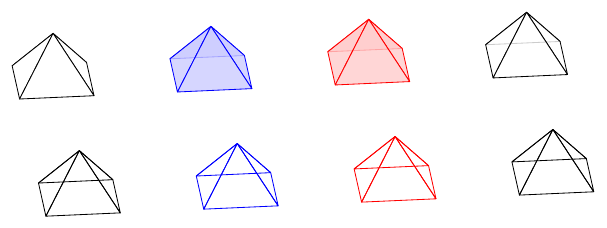
Available objects:
{box}{sphere}{cylinder}{cone}{pyramid}{coordsys}
Source: basic-shapes.sk
Using the objects
Every object is a drawable (see sketch manual).
Simplest usage: just type the object name
{box}For translating, rotating or scaling the object, use put:
put {translate([5,5,0]) * rotate(10, [X])}
{box}Customizing the objects
If you want to customize the default options, or change the style for a particular object, use the alternate form:
{ input{lib/object_name} }Examples:
Triangular pyramid
{
def n 3
input{lib/pyramid}
}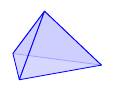
Source: pyramid3.sk
Alien sphere:
{
def style [cull=false, fill=green, fill opacity=0.9]
def segments 10
input{lib/sphere}
}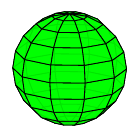
Source: sphere-custom.sk
The objects have the following options / parameters / tags:
-
all solid objects (box, sphere, cylinder, cone, pyramid):
-
def style [...]def style [cull=false, draw=red, fill=green, fill opacity=0.9] -
def wireframe<>
-
-
sphere:
-
def varsphere<>- alternative appearance for the sphere (experimental) -
def segments- sphere resolution (default 20)
-
-
cylinder and cone:
-
def segments- see sphere -
def generatrix<>- display the generatrix linesNote:
wireframe<>impliesgeneratrix<>(and also disables filling). -
def interior_scale 0.995- It is useful for reducing artifacts created by thick lines. The interior of the cylinder is drawn a bit smaller than the wireframe. If you have thick lines, try a smaller value. Use 1 to disable this scaling trick.
-
-
pyramid
def n- number of faces
-
coordsys
def rgb<>- show a color coordinate system (XYZ)
Overriding default settings
As you know, if you try to override a def, sketch will complain with an error message.
def foo 5
def foo 7 % error!However, you may override them in a child block.
def foo 5
{
def foo 7
% it works!
}
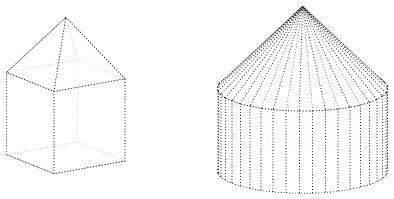
% here, foo is 5 againTherefore, we’ll do a similar trick to override the defaults for the entire scene:
input{lib/defaults.sk}
{
def style [cull=false, style=thick, style=dotted, draw=black, fill=white, fill opacity=0.8]
def generatrix<>
def segments 40
input{lib/objects.sk}
put{scale(1/sqrt(2))}{pyramid}
put{translate([0,0,-0.5])}{box}
put{translate([-2,-2,0])}
{
{cone}
put{translate([0,0,-0.5])}{cylinder}
}
}
global {
language tikz
camera view((-3,2,1), (o), [Z]) * scale(3)
}
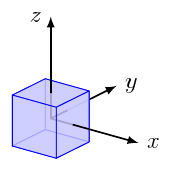
Annotating objects
For placing labels on a coordinate system, you may use something like this:
def blue<>
input{lib/defaults.sk}
input{lib/objects.sk}
put{translate([15,10,0])}
{
{box}
put{scale(2)}
{
{coordsys}
special |\path #1 node[right] {$x$}
#2 node[right] {$y$}
#3 node[left] {$z$};|(x)(y)(z)
}
}
global {
language tikz
camera view((1.5,-2,1), (o), [Z])
}
So, when you put special|...tikz-statements...|(x)(y)(z) inside a put, the points (x), (y) and (z) will be in the local reference frame of your object.
You will have to adjust manually the position of the label nodes: [right], [left], [above] or [below].
Of course, you may also specify global coordinates. For this, put the annotation commands on the outermost level:
line [arrows=<->, style=dashed] (0,0,2)(5,0,2)or, with TikZ code for more flexibility:
special|\draw [dashed, <->] #1 -- node[above, sloped]{$dx$} #2;|(0,0,2)(5,0,2)Be careful when typing TikZ code, since LaTeX error messages are not always intuitive.
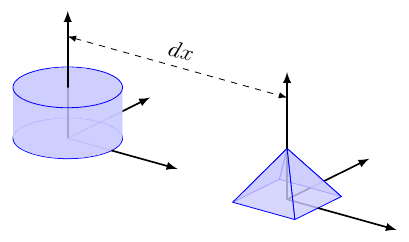
Source: annotate.sk
Robot kinematics diagram
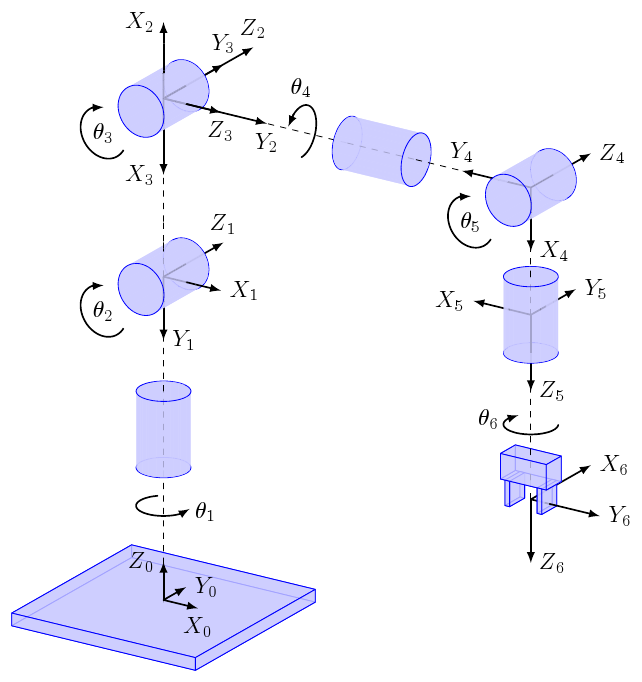
Source: kinematics.sk
Each link i has position and orientation relative to its parent (i-1).
Try changing the joint angles (J1…J6) and redraw the diagram!
Bugs / Limitations
This library is in alpha stage, so there are many bugs and limitations.
Here are some of them:
- It only works with PGF/TikZ. It was not tested with PSTricks, but it might work after some small tweaks.
- You cannot define custom styles with a name (you can only redefine
style) - It doesn’t like dashed lines (it seems to work, but it looks bad)
- Sketch gives a lot of warnings about unused items and unknown options
- Uses some hacks for parametrized objects
Please report all the bugs here. I will be happier if you would try to fix these bugs and send patches, though :)
Useful resources
For Sketch and TikZ:
- Introduction to Sketch for PGF/TikZ
- Sketch manual
- TikZ 3D examples
- PGF/TikZ manual
- Blender to Sketch exporter
For 3D graphs in LaTeX you may want to check:
